Classification
1 Overview
Description
Classification is a fundamental machine learning technique aimed at organizing input data into distinct classes. During the classification process, the model undergoes training using the 'train subset' function, followed by evaluation using the 'test subset' function. A notable distinction between classification and regression tasks lies in their output variables. While classification deals with discrete target variables, regression tasks involve continuous output variables.
Expected Outcome
Essentially, the expected outcome is to recognize patterns in the training data, and use these patterns to classify new data into one of the pre-defined classes.
Scenarios
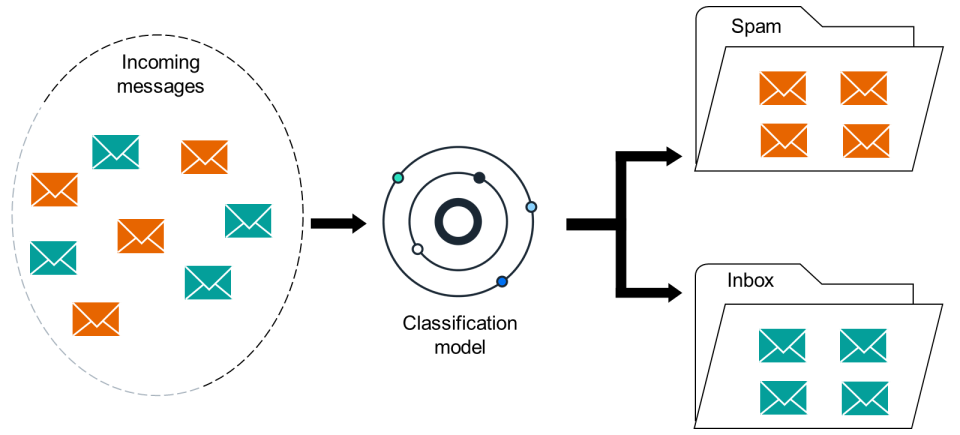
Classification can be utilized in various scenarios, such as spam detection, image recognition, fraud detection, medical diagnosis, among others. For example, the figure below illustrates how a classification model determines whether an incoming message falls under the category of SPAM or Inbox (non-SPAM).
The core principles of classification involve supervised learning, where models are trained using labeled data to recognize patterns and make predictions on new, unseen data.